Our Health Library information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Please be advised that this information is made available to assist our patients to learn more about their health. Our providers may not see and/or treat all topics found herein.
Nosebleeds
Overview
Most nosebleeds aren't serious. They usually can be stopped with home treatment. Most nosebleeds occur in the front of the nose (anterior epistaxis) and involve only one nostril. Some blood may drain down the back of the nose into the throat. Many things may make a nosebleed more likely. They include:
- Changes in the environment, such as:
- Cold, dry climates; low humidity.
- High altitude.
- Chemical fumes.
- Smoke.
- Injury to the nose, such as:
- Hitting or bumping the nose.
- Blowing or picking the nose.
- Piercing the nose.
- An object in the nose. This is more common in children, who may put things up their noses.
- Medical problems, such as:
- An abnormal structure inside the nose. Examples are nasal polyps and a deviated nasal septum.
- Colds, allergies, or sinus infections.
- High blood pressure.
- Kidney disease.
- Liver disease.
- Blood clotting disorders. These include hemophilia, leukemia, thrombocytopenia, and von Willebrand's disease.
- Abnormal blood vessels in the nose.
- Medicines, such as:
- Those that affect blood clotting. These include aspirin, other blood thinners, and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- Cold and allergy medicines.
- Oxygen.
- Nasal inhalers, such as Afrin.
- Steroid nasal sprays.
- Nasal use of illegal drugs, such as cocaine and amphetamines.
A less common but more serious type of nosebleed starts in the back of the nose (posterior epistaxis). It often involves both nostrils. Large amounts of blood may run down the back of the throat. This type occurs more often in older adults because of other health problems they may have. Medical treatment will be needed to control the bleeding from this type of nosebleed.
Check Your Symptoms
The medical assessment of symptoms is based on the body parts you have.
- If you are transgender or nonbinary, choose the sex that matches the body parts (such as ovaries, testes, prostate, breasts, penis, or vagina) you now have in the area where you are having symptoms.
- If your symptoms aren’t related to those organs, you can choose the gender you identify with.
- If you have some organs of both sexes, you may need to go through this triage tool twice (once as "male" and once as "female"). This will make sure that the tool asks the right questions for you.
Many things can affect how your body responds to a symptom and what kind of care you may need. These include:
- Your age. Babies and older adults tend to get sicker quicker.
- Your overall health. If you have a condition such as diabetes, HIV, cancer, or heart disease, you may need to pay closer attention to certain symptoms and seek care sooner.
- Medicines you take. Certain medicines, such as blood thinners (anticoagulants), medicines that suppress the immune system like steroids or chemotherapy, herbal remedies, or supplements can cause symptoms or make them worse.
- Recent health events, such as surgery or injury. These kinds of events can cause symptoms afterwards or make them more serious.
- Your health habits and lifestyle, such as eating and exercise habits, smoking, alcohol or drug use, sexual history, and travel.
Try Home Treatment
You have answered all the questions. Based on your answers, you may be able to take care of this problem at home.
- Try home treatment to relieve the symptoms.
- Call your doctor if symptoms get worse or you have any concerns (for example, if symptoms are not getting better as you would expect). You may need care sooner.
To stop a nosebleed:
- Gently blow your nose to clear any clots.
- Sit up straight, and tip your head slightly forward. (Do not tilt your head back. This may cause blood to run down your throat and make you vomit.)
- Pinch the front, soft part of your nose shut with your thumb and index finger for at least 15 minutes.
- After 15 minutes, check to see if your nose is still bleeding. If it is, pinch it shut for 10 to 15 more minutes. Most nosebleeds will stop after 10 to 20 minutes of pressure.
Symptoms of difficulty breathing can range from mild to severe. For example:
- You may feel a little out of breath but still be able to talk (mild difficulty breathing), or you may be so out of breath that you cannot talk at all (severe difficulty breathing).
- It may be getting hard to breathe with activity (mild difficulty breathing), or you may have to work very hard to breathe even when you're at rest (severe difficulty breathing).
Severe trouble breathing means:
- You cannot talk at all.
- You have to work very hard to breathe.
- You feel like you can't get enough air.
- You do not feel alert or cannot think clearly.
Moderate trouble breathing means:
- It's hard to talk in full sentences.
- It's hard to breathe with activity.
Mild trouble breathing means:
- You feel a little out of breath but can still talk.
- It's becoming hard to breathe with activity.
Severe trouble breathing means:
- The child cannot eat or talk because he or she is breathing so hard.
- The child's nostrils are flaring and the belly is moving in and out with every breath.
- The child seems to be tiring out.
- The child seems very sleepy or confused.
Moderate trouble breathing means:
- The child is breathing a lot faster than usual.
- The child has to take breaks from eating or talking to breathe.
- The nostrils flare or the belly moves in and out at times when the child breathes.
Mild trouble breathing means:
- The child is breathing a little faster than usual.
- The child seems a little out of breath but can still eat or talk.
A nosebleed is severe if:
- You have moderate to large amounts of blood even after you have pinched the nose shut for 10 minutes.
- Your nose is still bleeding even after 15 full minutes of direct pressure.
A nosebleed is moderate if:
- You have some bleeding, but direct pressure stops it within 15 minutes.
- The nose bleeds small amounts of blood more than 3 times in 24 hours.
A nosebleed is mild if:
- You have a little bleeding, but direct pressure stops it within 10 minutes.
- The nose bleeds no more than 3 times in 24 hours, and each time the bleeding is mild.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may quickly occur after a sudden illness or injury.
Adults and older children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Feeling very dizzy or lightheaded, like you may pass out.
- Feeling very weak or having trouble standing.
- Not feeling alert or able to think clearly. You may be confused, restless, fearful, or unable to respond to questions.
Shock is a life-threatening condition that may occur quickly after a sudden illness or injury.
Babies and young children often have several symptoms of shock. These include:
- Passing out (losing consciousness).
- Being very sleepy or hard to wake up.
- Not responding when being touched or talked to.
- Breathing much faster than usual.
- Acting confused. The child may not know where he or she is.
Abnormal bleeding means any heavy or frequent bleeding or any bleeding that is not normal for you. Examples of abnormal bleeding include:
- Nosebleeds.
- Vaginal bleeding that is different (heavier, more frequent, at a different time of month) than what you are used to.
- Rectal bleeding and bloody stools.
- Bloody or pink urine.
- Gums that bleed easily when you eat or gently brush your teeth.
When you have abnormal bleeding in one area of your body, it's important to think about whether you have been bleeding anywhere else. This can be a symptom of a more serious health problem.
Seek Care Now
Based on your answers, you may need care right away. The problem is likely to get worse without medical care.
- Call your doctor now to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or you don't have one, seek care in the next hour.
- You do not need to call an ambulance unless:
- You cannot travel safely either by driving yourself or by having someone else drive you.
- You are in an area where heavy traffic or other problems may slow you down.
Seek Care Today
Based on your answers, you may need care soon. The problem probably will not get better without medical care.
- Call your doctor or telehealth provider today to discuss the symptoms and arrange for care.
- If you cannot reach your doctor or telehealth provider or you don't have one, seek care today.
- If it is evening, watch the symptoms and seek care in the morning.
- If the symptoms get worse, seek care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Call 911 Now
Based on your answers, you need emergency care.
Call 911 or other emergency services now.
Sometimes people don't want to call 911. They may think that their symptoms aren't serious or that they can just get someone else to drive them. Or they might be concerned about the cost. But based on your answers, the safest and quickest way for you to get the care you need is to call 911 for medical transport to the hospital.
Make an Appointment
Based on your answers, the problem may not improve without medical care.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor in the next 1 to 2 weeks, or contact your telehealth provider.
- If appropriate, try home treatment while you are waiting for the appointment.
- If symptoms get worse or you have any concerns, call your doctor or telehealth provider. You may need care sooner.
What are your options for medical care?
Today your options for where to get your medical care are greater than ever before. You may not even have to leave your home to get the care you want and need. You can choose based on what your health problem is and what works best for you.
- Telehealth is a video call with a health care provider. It can be a convenient way to get medical advice or treatment. Some insurers provide access to telehealth that may be available 24 hours a day. Telehealth for less serious problems may cost less and be faster than in-person clinic visits.
- Urgent care and retail clinics are options if you don't have a doctor, you can't or don't want to wait to see your own doctor, or a telehealth visit can’t treat the problem.
- Virtual care from your primary provider or a telehealth service can be delivered through your smartphone, computer, or tablet.
Self-Care
How to stop a nosebleed
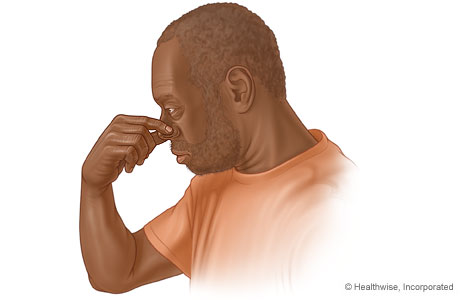
Follow these steps to stop a nosebleed.
- Gently blow your nose to clear any clots.
- Sit up straight and tip your head slightly forward.
Do not tilt your head back. This may cause blood to run down the back of your throat, and you may swallow it. Swallowed blood can irritate your stomach and cause vomiting. And vomiting may make the bleeding worse or cause it to start again. Spit out any blood that gathers in your mouth and throat rather than swallowing it.
- Use your thumb and forefinger to firmly pinch the soft part of your nose shut.
The nose consists of a hard, bony part and a softer part made of cartilage. Nosebleeds usually occur in the soft part of the nose.
Spraying the nose with a decongestant nasal spray like oxymetazoline (Afrin) before applying pressure may help stop a nosebleed. Be safe with medicines. Read and follow all instructions on the label.
You will have to breathe through your mouth.
- Keep pinching for at least 15 minutes.
Use a clock to time the 15 minutes. It can seem like a long time. Resist the urge to peek after a few minutes to see if your nose has stopped bleeding.
- Check to see if your nose is still bleeding after 15 minutes.
If it is, hold it for 10 to 15 more minutes. Most nosebleeds will stop after 10 to 20 minutes of direct pressure.
- Put a thin layer of a saline- or water-based nasal gel, such as NasoGel, or an antiseptic nasal cream inside your nose.
Do not blow your nose or put anything else inside your nose for several hours after the bleeding has stopped.
- Rest quietly for a few hours.
When to call for help during self-care
Call a doctor if any of the following occur during self-care at home:
- Your nose is still bleeding after you have pinched the nose shut 2 times for 15 minutes each time (30 minutes total).
- Nosebleeds occur 4 or more times in 1 week.
- Symptoms occur more often or are more severe.
Preparing For Your Appointment
You can help your doctor diagnose and treat your condition by being prepared for your appointment.
Related Information
Credits
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: October 27, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
This information does not replace the advice of a doctor. Ignite Healthwise, LLC disclaims any warranty or liability for your use of this information. Your use of this information means that you agree to the Terms of Use and Privacy Policy. Learn how we develop our content.
To learn more about Ignite Healthwise, LLC, visit webmdignite.com.
© 2024-2025 Ignite Healthwise, LLC.